Modern spatial analytics
built for the cloud


Cloud native analytics with no limits
CARTO extends the native analysis and visualization capabilities available in BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift, Databricks, and more. Access a single, secure source for all your spatial analysis, giving you speed and agility, with limitless data scale.
.png)
.jpg)
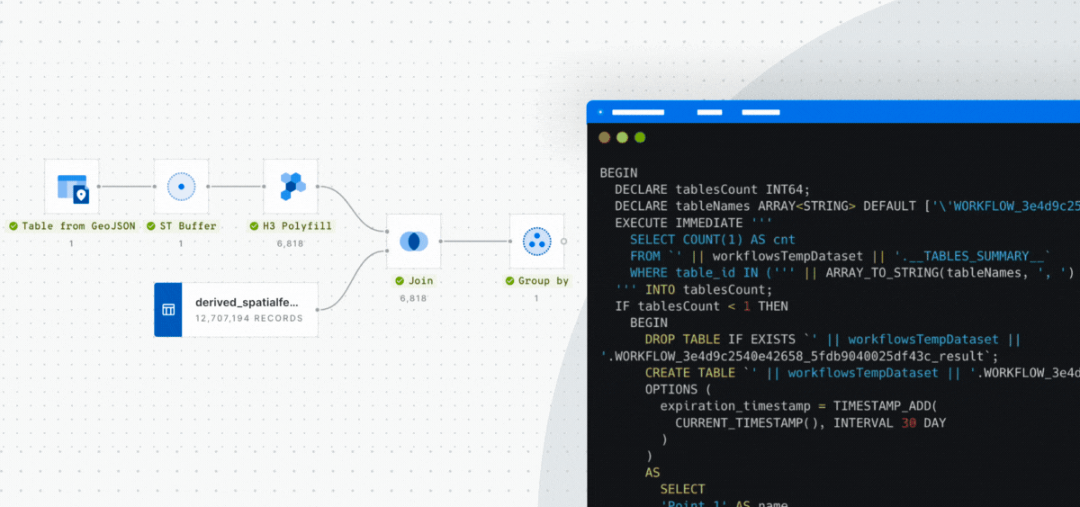
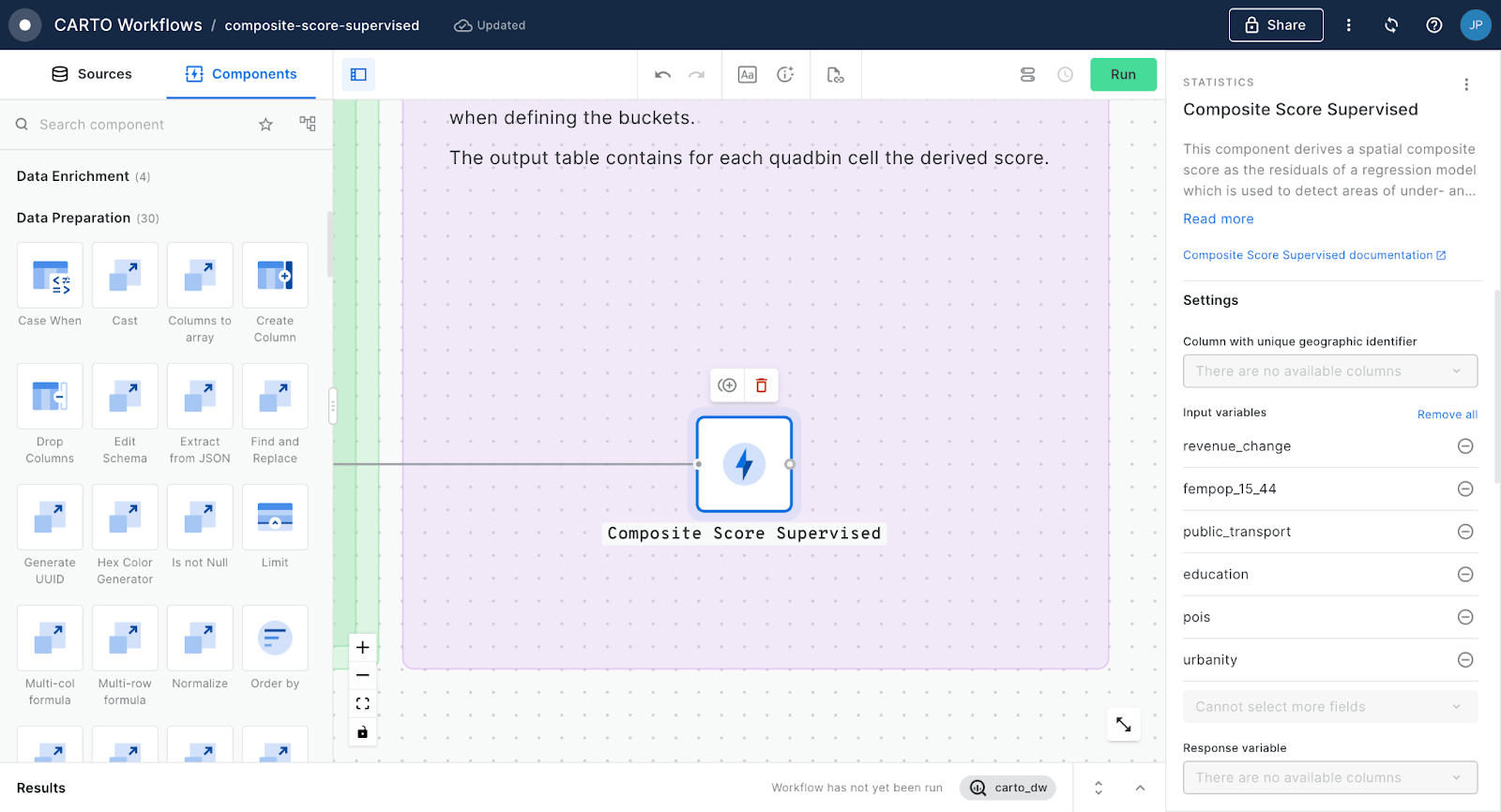
Powerful analytics with a visual workflow design tool
Easily design and automate advanced data processing and analysis pipelines natively on the leading cloud platforms using our intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
%20(1)%20(1).webp)
%20(1).webp)

Fully cloud native
Design, run and scale workflows natively in your data warehouse. No code, no data duplication, or complex ETLs.

100+ ready-to-go analysis components
Intuitive analytics for any skill level. From data preparation to analysis functions in a complete suite of drag-and-drop components.

Built-in GenAI capabilities
Unleash the power of cloud native LLMs and Machine Learning models for improved productivity & quicker insights.
%202%20(1).webp)

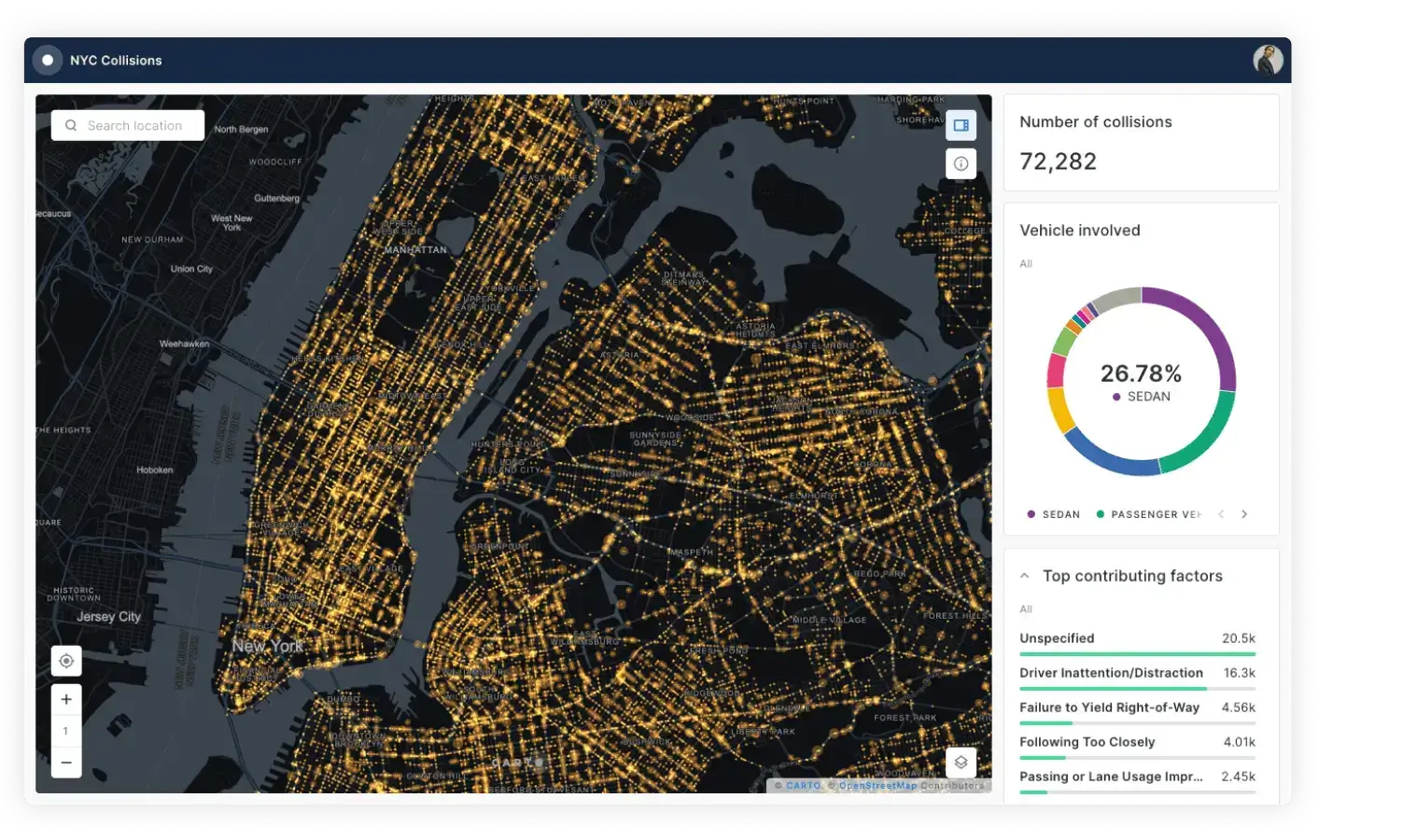
Easily connect your spatial data
Access your cloud-hosted spatial data using an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.

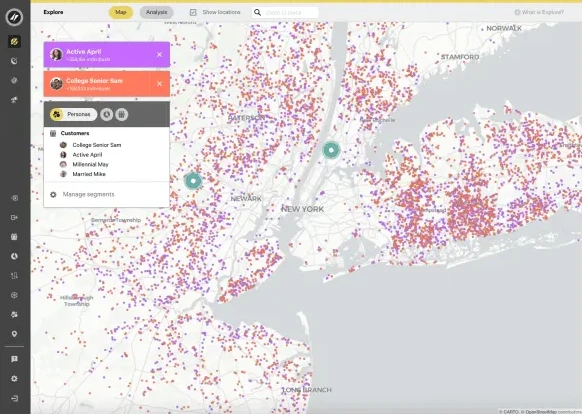
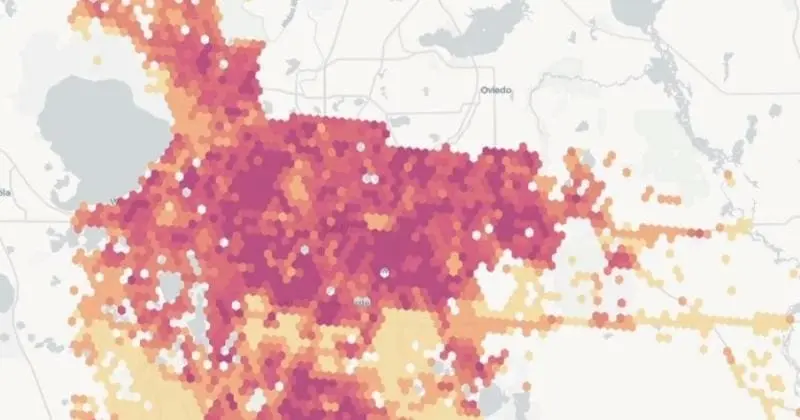
Visualize billions of data points with ease
Build performant, interactive map visualizations without any limits on data volumes.

Publish & share your insights
Share visualizations and dashboards securely, or embed them in your own applications.
Accelerated, scalable app development
Reduce the time and cost to develop spatial applications with our APIs and development toolkit. Build powerful map-centric applications running in your cloud data architecture, without any limits on scalability.
.webp)
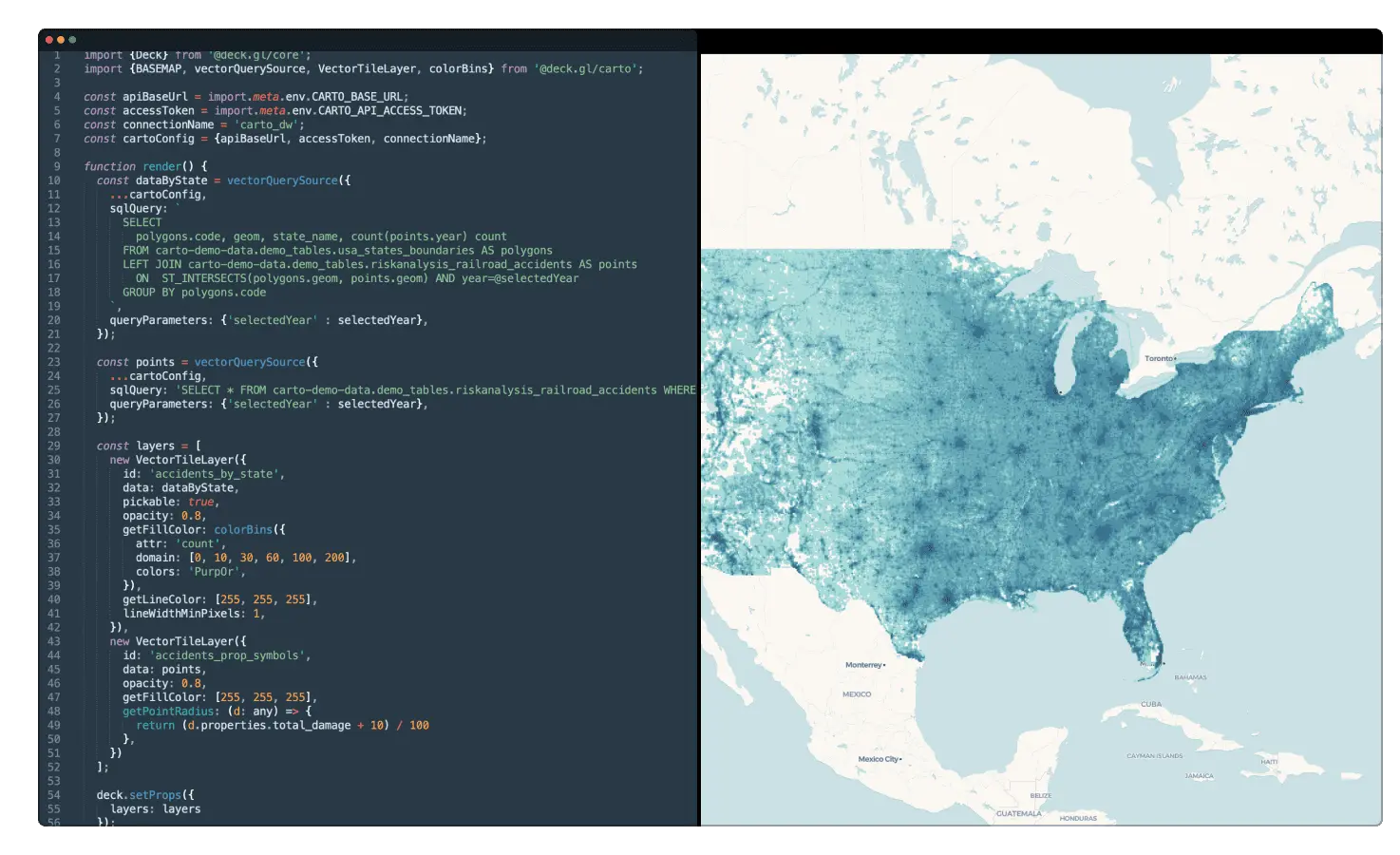

Frame agnostic development
Build your application using vanilla Javascript, Typescript or your framework of choice (Vue, React, Angular…).

Without intermediate mapping servers
Built from the ground up to visualize massive datasets, directly from your cloud data warehouse.

Innovative visualization tools
Render using deck.gl, leveraging the latest WebGL and WebGPU technology, for unparalleled performance.
Trusted by market leaders

















Truly enterprise-ready
Enterprise-grade security, authentication and data access controls let you distribute your analysis securely with stakeholders. With CARTO Self-Hosted you get the same versatile data analysis experience, running in your own controlled environment.
.png)
Check out our resources & join our
growing spatial community
TALK TO US
Request a demo
Schedule a 20 minute meeting with our experts to understand how you can use spatial analysis in your organization.















.gif)






.png)